Managing Certificate Authority details
The Certificate Authorities page allows you to:
-
HUB Certificate Authority tab: Create your own CA or upload the root certificate of a trusted third-party CA.
-
DFSP Certificate Authority tab: Retrieve the root and intermediate certificates of DFSPs' CAs for importing into your trust store.
Setting up a Hub Certificate Authority (CA)
The Certificate Authorities page allows you to:
-
HUB Certificate Authority tab: set up an embedded CA for the Hub
-
HUB External Certificate Authority tab: upload the root and intermediate certificates of a trusted third-party CA
A Hub CA is required so that you can create client certificate signing requests (CSRs) using the parameters provided in the MCM portal.
The Certificate Authorities page > HUB Certificate Authority tab lets you set up an embedded CA for the Hub.
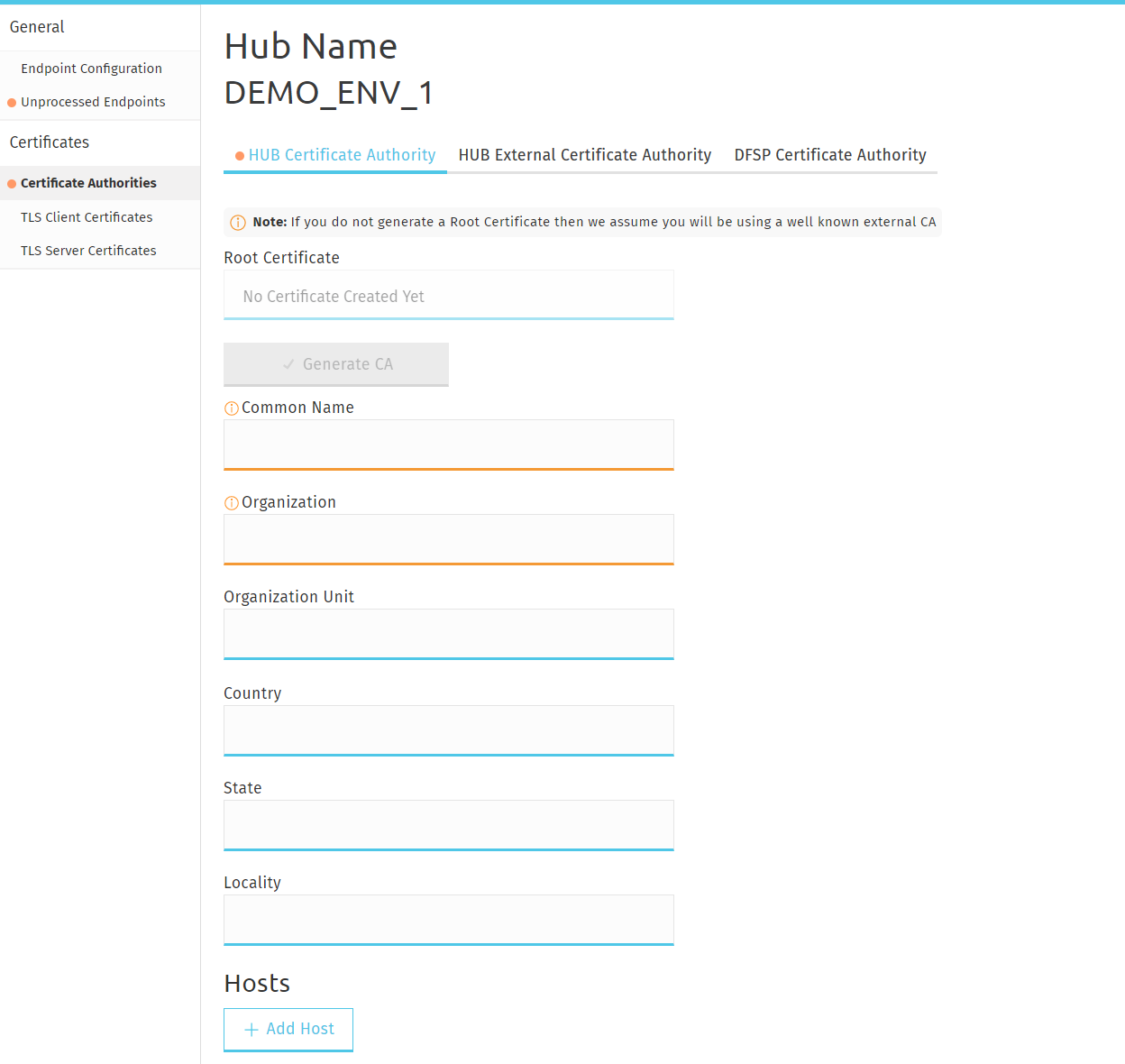
| Once a Certificate Authority has been entered, there is currently no possibility to delete it. |
To create an embedded CA:
-
Enter the required parameters in the following fields to create the root certificate for the CA:
-
Common Name
-
Organization
-
Organization Unit
-
Country
-
State
-
Locality
-
-
Optionally, click Add Hosts to add hostnames for information sharing.
-
Click Generate CA.
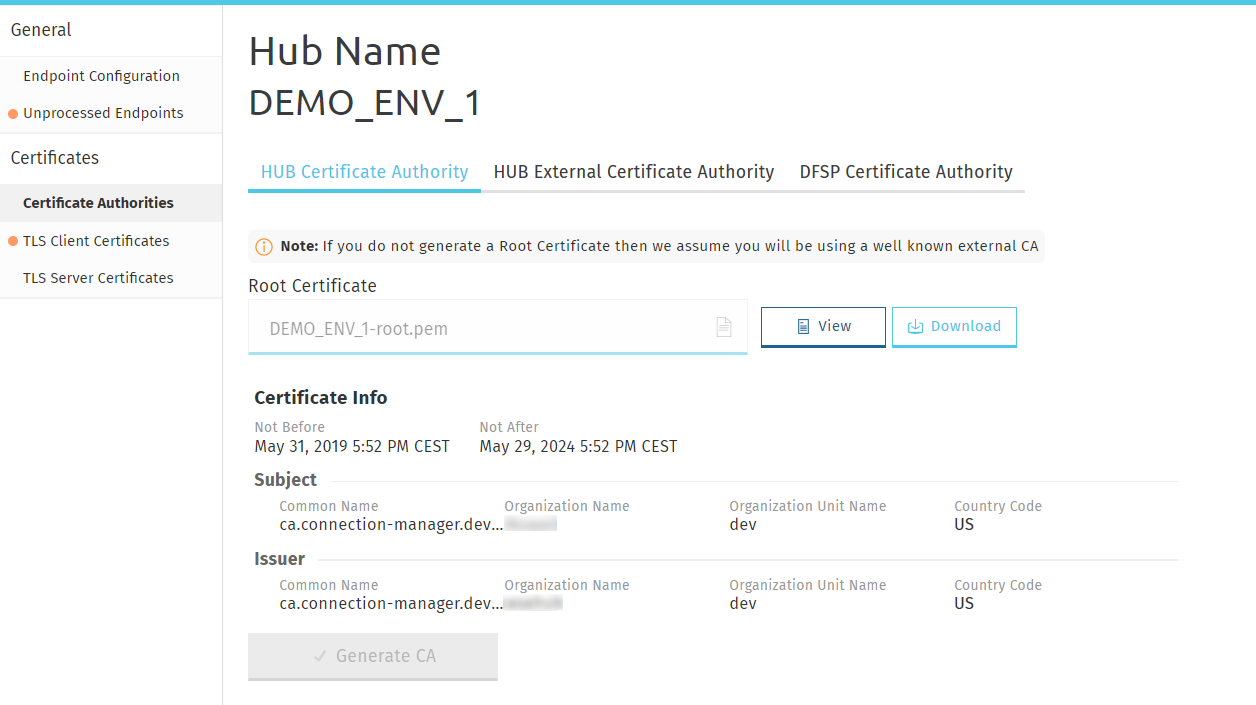
Click View to view details of the certificate. Click Download to download the certificate for manual handover to DFSPs (if required).
The Certificate Authorities page > HUB External Certificate Authority tab lets you upload the root and intermediate certificates of a trusted third-party CA.
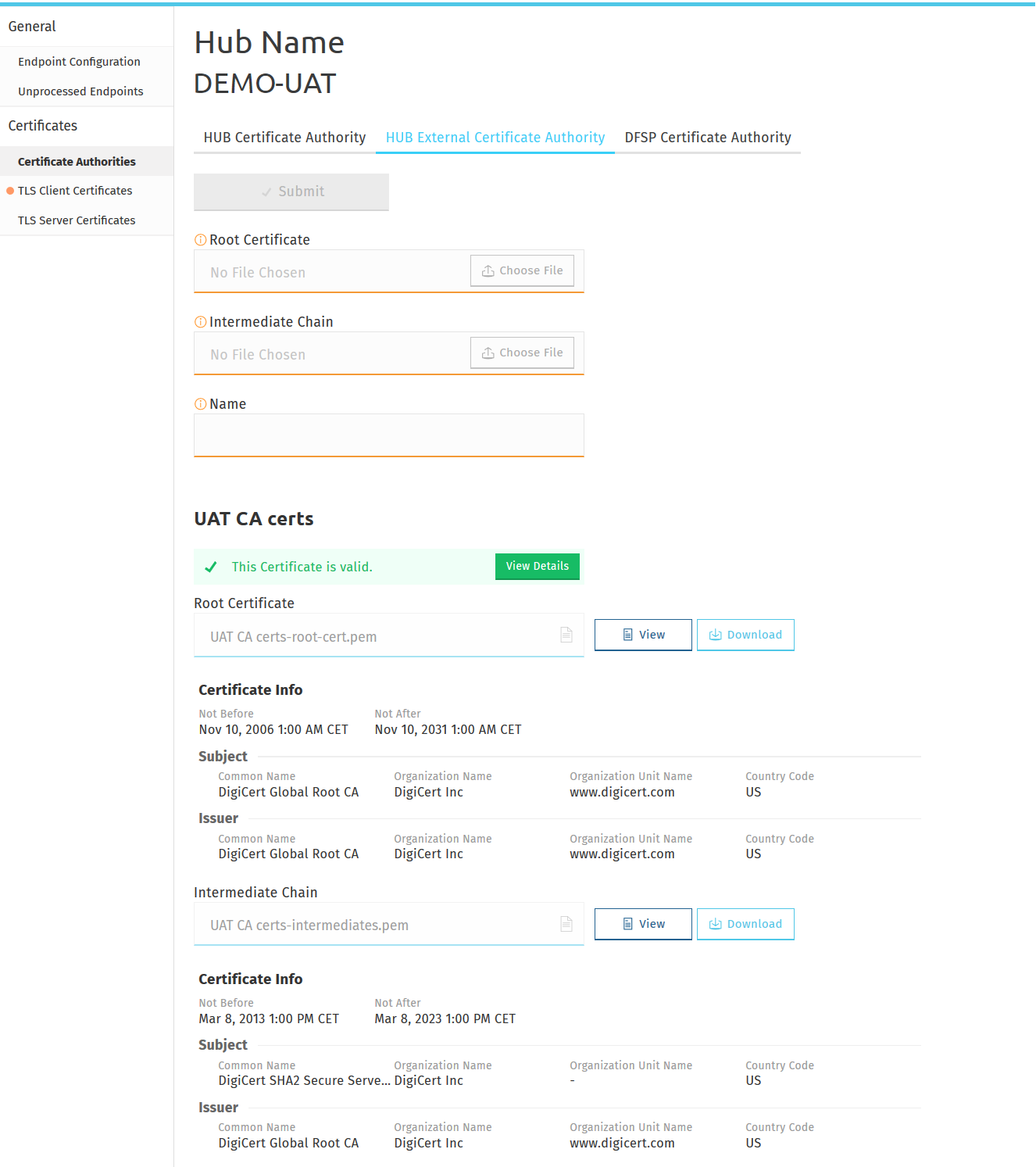
To upload the root certificate and intermediate chain of an external CA, complete the following steps:
| On uploading a certificate, MCM renames the file so that the file name includes information about: 1) the type of certificate (for example: root, intermediate, server), 2) the environment (for example: sandbox, staging, production), 3) the name of the DFSP. |
This means that when uploading a certificate to MCM, you will see the original file name of your certificate change to a value assigned by MCM.
-
To upload the root certificate of your external CA, click Choose File in the Root Certificate field, and select the root certificate of your CA saved on your computer.
-
To upload the intermediate certificate of your external CA, click Choose File in the Intermediate Chain field, and select the intermediate certificate of your CA saved on your computer.
NOTE: The intermediate chain must be presented as a single file. If your intermediate chain is made up of multiple files, combine them into one file in the following order: host certificate first, then the certificate that signs it, then the certificate that signs the previous certificate, and so on. Go from the most specific certificate to the least specific certificate, with each certificate verifying the previous one. -
In the Name field, type a meaningful name for your external CA.
-
Click Submit. On submitting the certificates, they are validated. The following details are validated:
-
The root certificate is a root certificate indeed. It can be self-signed or signed by a global root.
-
The root certificate has the CA basic contraint extension ( CA = true ).
-
The intermediate chain is made up of valid CAs and the top of the chain is signed by the root.
-
The certificate and its chain must form a valid trust chain.
-
-
The certificates are displayed at the bottom of the page. To view or download them, click View or Download.
| If you have accidentally uploaded the wrong certificate, you can re-upload a new certificate and that will replace the old one. |
Retrieving the certificates of a DFSP’s CA
The Certificate Authorities page > DFSP Certificate Authority tab gives you access to the root and intermediate certificates of DFSPs' CAs for importing into your trust store after they have uploaded it.
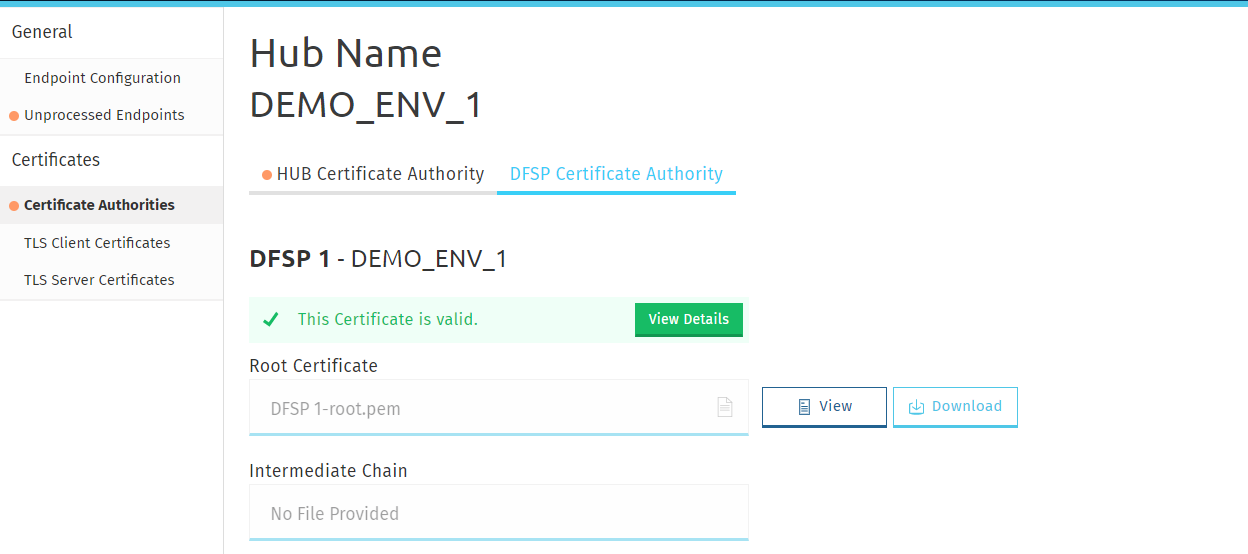
Click View to view details of the certificate, or click Download to download the certificate.
Information about the validity of the certificate is also displayed. Click View Details for details on validation. The following details are validated:
-
The root certificate is a root certificate indeed. It can be self-signed or signed by a global root.
-
The root and intermediate CA certificates must have the CA basic constraint extension (
CA = true) and the keyCertSign key usage extension. -
The intermediate chain is made of valid CAs and the top of the chain is signed by the root.