Introduction
At a high level, onboarding to a Mojaloop-based scheme requires a Digital Financial Service Provider (DFSP) to focus their efforts around the following major milestones:
-
Integration of their Core Backend with the Mojaloop Switch on the API level (this involves both coding and testing).
-
Connecting to Mojaloop pre-production and production environments following rigorous Mojaloop security requirements.
Payment Manager for Mojaloop provides functionality to simplify both of these steps. This document provides details about API-level integration.
The following diagram provides a high-level view of the integration between a Mojaloop Real-Time Payment System and a DFSP’s Core Backend.
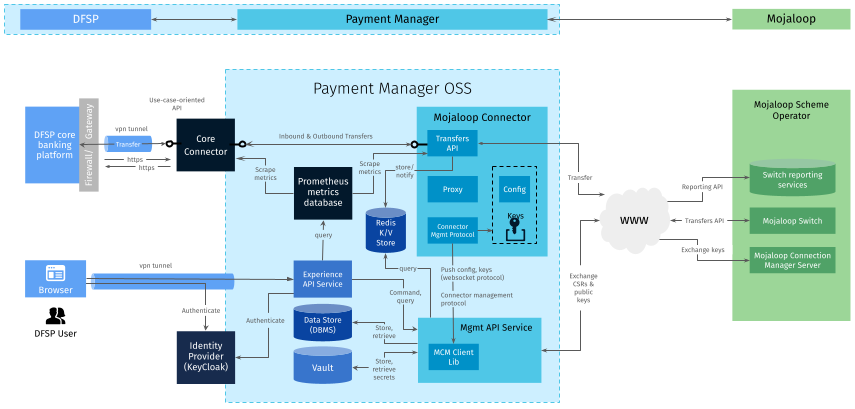
Payment Manager provides the following components:
-
Core Connector: Integrates a DFSP’s Core Backend to Payment Manager as an "adapter" for both parts so communication is possible between them. It uses standard templates, the majority of them written in Apache Camel, a declarative language for integration engineers that does not require writing code from scratch. There is a ready-made Core Connector template available for DFSPs to simplify their development effort.
-
Mojaloop Connector: Comes with the following key components:
-
A Mojaloop-SDK, which provides:
-
Mojaloop-compliant security components
-
HTTP header processing capabilities
-
A simplified use-case-oriented version of the Mojaloop FSPIOP API. DFSPs will be talking to this API, leveraging Core Connector.
-
-
A Connection Manager Client, which simplifies and automates certificate creation, signing and exchange, as well as the configuration of the connections required to different environments.
-
-
Portals: Provide dashboards for monitoring transactions and service status. They also allow DFSPs to manage their security keys, certificates, and endpoint configuration required for connecting to a Mojaloop-based scheme in a guided way.